The Technology market is constantly evolving at a faster speed than we can ever imagine. Emerging tech markets are offering important tools and frameworks for accessing a futuristic tech-driven world. One of the many emerging techs is Blockchain Technology.
Blockchain has been one of the biggest tech innovations of the 21st century creating a ripple effect across various industries After artificial intelligence and machine learning, blockchain has emerged as an important driver of digital transformation and has disrupted various ways of doing business.
History of Blockchain
In 1991, Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta created a chain of cryogenic ally secured blocks with timestamps of documents that could not be manipulated. It was only in 2008 that there was a renewed interest in blockchain thanks to the work of one person or a group by the name Satoshi Nakamoto.
Considered to be the brain behind the development of blockchain, Satoshi Nakamoto worked on Bitcoin, the first application of digital ledger technology. Nakamoto conceptualized the first blockchain and presented the first white paper on blockchain technology in 2009. Since then, new applications are being added to leverage the capabilities of blockchain.
What is Blockchain Technology?
Here’s how it works. Each block is encrypted with a chain that contains zillions of transactions.
Every time a transaction is made on the ledger, a record of that transaction is maintained and added to the participant’s ledger with an immutable cryogenic signature known as hash. A unique hash value is attributed to each block.
Types of Blockchain:
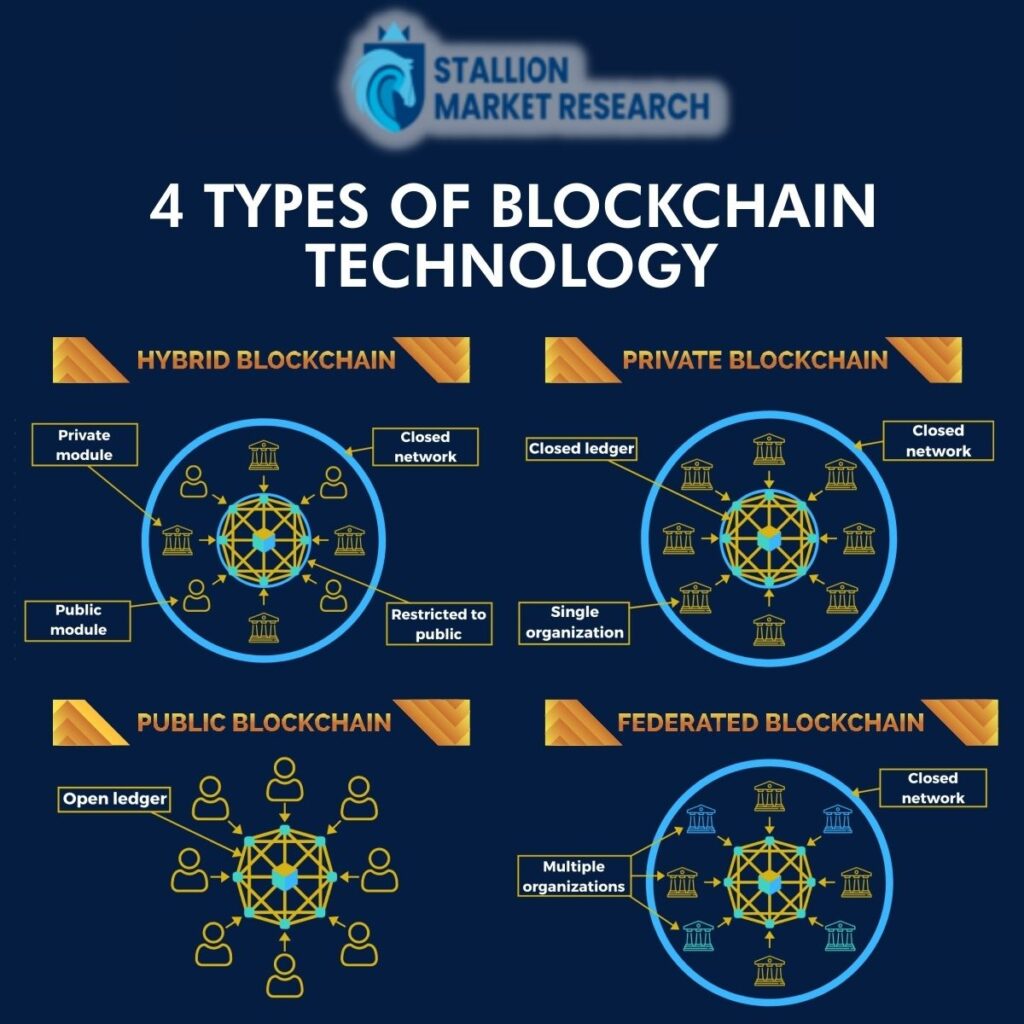
There are four types of blockchains:
- Public Blockchain: This is an open-source platform that is accessible to multiple users and is not restricted to any individual entity. Multiple users can read/write/audit the blockchain with no order for processing of transactions.
- Private Blockchain: Private blockchain restricts users who can participate and make transactions. A group of individuals or organizations have control of the blockchain network.
- Consortium/Federated Blockchain: This blockchain is a partially decentralized blockchain that is partly private and partly public, and exhibits the properties of a private and public blockchain; however, it leans more towards private blockchain by retaining most of its characteristics.
- Hybrid blockchain: Hybrid is a combination of public and private blockchain and combines the advantageous characteristics of both public and private blockchain. The privacy benefit of a private blockchain and the transparency benefit of a public blockchain is combined to give rise to a hybrid model of a blockchain.
Why Blockchain?
As digital money is gaining momentum, creating a foolproof system was the need of the hour. A system based on trust that if a new currency has been created, one cannot cheat or hack or steal currency. That need led to the creation of a cryptocurrency called Bitcoin which was built using a specific type of database called Blockchain.
What makes Blockchain different from the rest of the databases is that, unlike other databases where only a single person is in charge of changing the entries and thereby likely to cheat or hack using the system, blockchain is run by multiple people who use it. This is what makes blockchain technology immune to hackers and trustworthy.
Benefits of Blockchain:
- Transparency: Transparency is the main bedrock of blockchain technology. Transaction histories become transparent as blockchain is a distributed ledger where all the network participants share the same document that can only be changed through consensus. To make even the smallest of a change would require alteration of all subsequent records.
- Security: Blockchain is a safe and secure record-keeping system. Only transactions that have been approved, are encrypted and linked to the previous transaction. Information is stored across a network of computers rather than one server, making it difficult for hackers to access the transaction data. The safety of sensitive data is imperative to any industry.
- Improved traceability: As blockchain creates a record of the entire transaction data, it helps tremendously when the origin of the asset to every stop it makes on its journey is captured during an audit trail.
- Increased speed and efficiency: A paper-heavy process is always more time-consuming and is prone to human error that often requires mediation. Streamlining and automating these processes with blockchain helps in completing the transactions faster without much clutter and improves efficiency.
- Reducing costs: Three properties of Blockchain-transparency, immutability, and security makes this database a reliable application that can help consumer markets reduce the cost of their transactions to near zero and opens the door to real-time micropayment. The financial transaction comes at a cost as retailers routinely need to pay some percentage to credit card companies or vendors need to pay sales fees using eBay or Shopify whereas for consumers, they need to pay the transaction fees. These hidden fees add to the cost of the goods and are often passed on to the consumer. Blockchain helps to reduce these transaction costs by cutting intermediaries and liaising directly with the banks using the blockchain’s layer of security during both ends of the transactions thereby considerably reducing cross-border fees by removing the need for third-party vendors and maintaining records, organizations can bring down their costs using blockchain.
Growth Story of Blockchain:
With each year, blockchain technology has only seen growth. The global blockchain market size is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) rate of 69% between 2019 and 2025 and will become a mainstay of business across all sectors. By 2022, global spending on blockchain solutions is expected to reach ~$12 billion. By 2024, blockchain will accumulate close to ~$21 million in revenue.
Industries that Benefit:
Beyond cryptocurrency, blockchain can function in multiple sectors. Finance majors like banking and payments have already demonstrated interest in blockchain technology. Integrating blockchain into healthcare is another sector that can majorly gain from this technology. Blockchain wallets that are digital wallets capable of storing cryptocurrency transactions are accelerating at a fast pace.
Using blockchain technology can also improve the planning and experience of virtual events that will improve the experience of the attendee, reduce operational cost and assures the safety of your data.
From manufacturing to agriculture, insurance and many more sectors, blockchain’s usefulness has been seen in every sector where it has been applied.

